The student exploration inclined plane simple machine delves into the fascinating world of simple machines, exploring the concept of inclined planes and their practical applications. As we embark on this journey, we will uncover the forces that govern the motion of objects on inclined planes and delve into the mechanical advantage they provide.
This exploration promises to shed light on the efficiency and versatility of inclined planes, making us appreciate their significance in various fields.
Inclined Plane as a Simple Machine: Student Exploration Inclined Plane Simple Machine
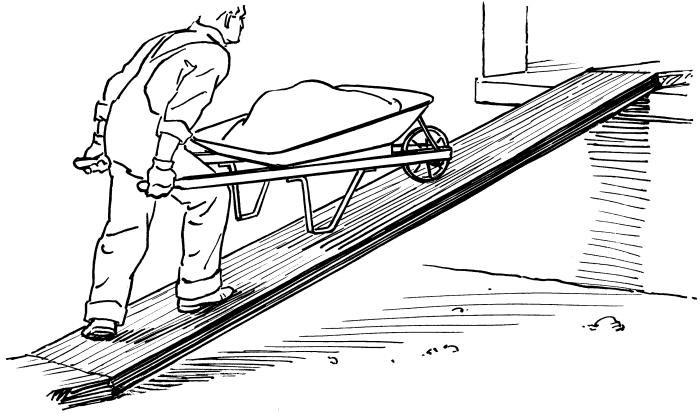
An inclined plane is a simple machine that consists of a sloping surface that connects two different levels. It allows objects to be moved from one level to another with less effort than lifting them directly. Inclined planes are used in a wide variety of applications, from ramps for wheelchairs to conveyor belts in factories.
Examples of Inclined Planes in Everyday Life
- Ramps for wheelchairs and strollers
- Conveyor belts in factories and warehouses
- Stairs
- Escalators
- Rooftops
Forces and Motion on an Inclined Plane
When an object is placed on an inclined plane, it is acted upon by three forces: gravity, normal force, and friction. Gravity pulls the object down the plane, while the normal force pushes the object perpendicular to the plane. Friction opposes the motion of the object.
The force of gravity acting on an object on an inclined plane is given by:
“`Fg = mg
sin(theta)
“`
where:
* Fg is the force of gravity
- m is the mass of the object
- g is the acceleration due to gravity
- theta is the angle of inclination of the plane
The normal force acting on an object on an inclined plane is given by:
“`Fn = mg
cos(theta)
“`
where:
* Fn is the normal force
- m is the mass of the object
- g is the acceleration due to gravity
- theta is the angle of inclination of the plane
The force of friction acting on an object on an inclined plane is given by:
“`Ff = mu
Fn
“`
where:
* Ff is the force of friction
- mu is the coefficient of friction
- Fn is the normal force
Mechanical Advantage of an Inclined Plane, Student exploration inclined plane simple machine
The mechanical advantage of an inclined plane is the ratio of the output force to the input force. The output force is the force required to move the object up the plane, while the input force is the force applied to the object.
The mechanical advantage of an inclined plane is given by:
“`MA = d / h“`
where:
* MA is the mechanical advantage
- d is the distance along the plane
- h is the height of the plane
The mechanical advantage of an inclined plane can also be calculated using the following formula:
“`MA = 1 / sin(theta)“`
where:
* MA is the mechanical advantage
theta is the angle of inclination of the plane
Efficiency of Inclined Planes
The efficiency of an inclined plane is the ratio of the output work to the input work. The output work is the work done by the object as it moves up the plane, while the input work is the work done by the force applied to the object.
The efficiency of an inclined plane is given by:
“`Efficiency = Output Work / Input Work“`
The efficiency of an inclined plane is affected by two factors: friction and the angle of inclination. Friction reduces the efficiency of an inclined plane because it opposes the motion of the object. The angle of inclination also affects the efficiency of an inclined plane.
The steeper the angle of inclination, the less efficient the inclined plane will be.
There are a number of ways to improve the efficiency of an inclined plane. One way is to reduce friction. This can be done by lubricating the plane or by using a material with a low coefficient of friction. Another way to improve the efficiency of an inclined plane is to decrease the angle of inclination.
However, this may not always be possible.
Applications of Inclined Planes
Inclined planes are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Construction: Inclined planes are used to move heavy objects, such as building materials, up to higher levels.
- Transportation: Inclined planes are used to move vehicles up and down hills. Ramps are used to allow wheelchairs and strollers to access buildings.
- Manufacturing: Inclined planes are used to move products from one level to another in factories and warehouses.
Inclined planes make tasks easier or more efficient by reducing the amount of force required to move objects.
FAQ Corner
What is the primary function of an inclined plane?
An inclined plane is designed to make lifting or moving objects easier by reducing the amount of force required.
How does the angle of inclination affect the mechanical advantage of an inclined plane?
The steeper the angle of inclination, the greater the mechanical advantage, making it easier to lift or move objects.
What factors can reduce the efficiency of an inclined plane?
Friction and the angle of inclination can both reduce the efficiency of an inclined plane.